UniRx – Unity响应式编程插件
插件作者Yoshifumi Kawai(neuecc)
本文译者:郑洪智 – 你的技术探路者

UniRx是什么?
UniRx (Unity响应式编程插件) 重写了.Net的响应式扩展。.Net官方的Rx很棒,但是在Unity中无法使用,并且与IOS的IL2CPP有兼容性问题。这个库这些问题并且添加了一些Unity专属的工具类。 支持的平台有:PC/Mac/Android/iOS/WP8/WindowsStore/等等,并且支持Unity4.6之后的所有版本。
UniRx 在 Unity Asset Store 的地址(免费) – http://u3d.as/content/neuecc/uni-rx-reactive-extensions-for-unity/7tT
演讲PPT – http://www.slideshare.net/neuecc/unirx-reactive-extensions-for-unityen
更新博客 – https://medium.com/@neuecc
在Unity论坛中提供支持 – http://forum.unity3d.com/threads/248535-UniRx-Reactive-Extensions-for-Unity
更新日志 UniRx/releases
UniRx 包含 Core Library (Port of Rx) + Platform Adaptor (MainThreadScheduler/FromCoroutine/etc) + Framework (ObservableTriggers/ReactiveProeperty/etc)
为什么用Rx?
一般来说,网络操作需要用到 WWW 和 Coroutine。但是使用 Coroutine 对于异步操作来说不是一个好的选择,原因如下:
- 协程不能有返回值,因为它返回类型必须是IEnumerator
- 协程不能处理异常,因为 yield return 语句没办法被 try-catch
会造成代码大面积的强耦合。
Rx就是为了解决异步问题而来的。Rx可以让异步操作更优雅,使用事件驱动编程,使用LINQ操作。
游戏循环 (every Update, OnCollisionEnter, etc), 传感器数据 (Kinect, Leap Motion, VR Input, etc.) 都是事件。Rx将事件转化为响应式的序列,通过LINQ操作可以很简单地组合起来,还支持时间操作。
Unity通常是单线程,但是UniRx可以让多线程更容易。
UniRx 可以简化 uGUI 的编程,所有的UI事件 (clicked, valuechanged, etc) 可以转化为 UniRx 的事件流。
简介
介绍 Rx 的非常棒的文章: The introduction to Reactive Programming you’ve been missing.
下面的代码实现了双击的检测:
var clickStream = Observable.EveryUpdate()
.Where(_ => Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0));
clickStream.Buffer(clickStream.Throttle(TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(250)))
.Where(xs => xs.Count >= 2)
.Subscribe(xs => Debug.Log("DoubleClick Detected! Count:" + xs.Count));
这个例子仅用5行代码,展示出了下面的特性:
- 将游戏循环为 (Update) 变成事件流
- 组合事件流
- 合并自身事件流
- 基于时间的操作非常简单
网络操作
使用 ObservableWWW 进行异步网络操作。它的 Get/Post 方法返回可订阅(Subscribe)的 IObservables:
ObservableWWW.Get("http://google.co.jp/")
.Subscribe(
x => Debug.Log(x.Substring(0, 100)), // onSuccess
ex => Debug.LogException(ex)); // onError
Rx 可以组合和取消。你也可以通过LINQ表达式进行查询:
// composing asynchronous sequence with LINQ query expressions
var query = from google in ObservableWWW.Get("http://google.com/")
from bing in ObservableWWW.Get("http://bing.com/")
from unknown in ObservableWWW.Get(google + bing)
select new { google, bing, unknown };
var cancel = query.Subscribe(x => Debug.Log(x));
// Call Dispose is cancel.
cancel.Dispose();
并行请求使用 Observable.WhenAll :
// Observable.WhenAll is for parallel asynchronous operation
// (It's like Observable.Zip but specialized for single async operations like Task.WhenAll)
var parallel = Observable.WhenAll(
ObservableWWW.Get("http://google.com/"),
ObservableWWW.Get("http://bing.com/"),
ObservableWWW.Get("http://unity3d.com/"));
parallel.Subscribe(xs =>
{
Debug.Log(xs[0].Substring(0, 100)); // google
Debug.Log(xs[1].Substring(0, 100)); // bing
Debug.Log(xs[2].Substring(0, 100)); // unity
});
也可以获取进度信息:
// notifier for progress use ScheudledNotifier or new Progress<float>(/* action */)
var progressNotifier = new ScheduledNotifier<float>();
progressNotifier.Subscribe(x => Debug.Log(x)); // write www.progress
// pass notifier to WWW.Get/Post
ObservableWWW.Get("http://google.com/", progress: progressNotifier).Subscribe();
错误处理:
// If WWW has .error, ObservableWWW throws WWWErrorException to onError pipeline.
// WWWErrorException has RawErrorMessage, HasResponse, StatusCode, ResponseHeaders
ObservableWWW.Get("http://www.google.com/404")
.CatchIgnore((WWWErrorException ex) =>
{
Debug.Log(ex.RawErrorMessage);
if (ex.HasResponse)
{
Debug.Log(ex.StatusCode);
}
foreach (var item in ex.ResponseHeaders)
{
Debug.Log(item.Key + ":" + item.Value);
}
})
.Subscribe();
和 IEnumerators 一起使用(协程)
IEnumerator (协程) 是Unity主要的异步工具。UniRx 集成了协程和 IObservables。 你可以用协程写异步代码,然后用 UniRx 来组织他们。这是控制异步流的最好的方法。
// two coroutines
IEnumerator AsyncA()
{
Debug.Log("a start");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1);
Debug.Log("a end");
}
IEnumerator AsyncB()
{
Debug.Log("b start");
yield return new WaitForEndOfFrame();
Debug.Log("b end");
}
// main code
// Observable.FromCoroutine converts IEnumerator to Observable<Unit>.
// You can also use the shorthand, AsyncA().ToObservable()
// after AsyncA completes, run AsyncB as a continuous routine.
// UniRx expands SelectMany(IEnumerator) as SelectMany(IEnumerator.ToObservable())
var cancel = Observable.FromCoroutine(AsyncA)
.SelectMany(AsyncB)
.Subscribe();
// you can stop a coroutine by calling your subscription's Dispose.
cancel.Dispose();
在 Unity 5.3 或更新版本里, 可以使用 ToYieldInstruction 将 Observable 转为 Coroutine。
IEnumerator TestNewCustomYieldInstruction()
{
// wait Rx Observable.
yield return Observable.Timer(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)).ToYieldInstruction();
// you can change the scheduler(this is ignore Time.scale)
yield return Observable.Timer(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1), Scheduler.MainThreadIgnoreTimeScale).ToYieldInstruction();
// get return value from ObservableYieldInstruction
var o = ObservableWWW.Get("http://unity3d.com/").ToYieldInstruction(throwOnError: false);
yield return o;
if (o.HasError) { Debug.Log(o.Error.ToString()); }
if (o.HasResult) { Debug.Log(o.Result); }
// other sample(wait until transform.position.y >= 100)
yield return this.transform.ObserveEveryValueChanged(x => x.position).FirstOrDefault(p => p.y >= 100).ToYieldInstruction();
}
通常,协程想要返回一个值需要使用回调callback。Observable.FromCoroutine 可以将协程转为可以取消的 IObservable[T]。
// public method
public static IObservable<string> GetWWW(string url)
{
// convert coroutine to IObservable
return Observable.FromCoroutine<string>((observer, cancellationToken) => GetWWWCore(url, observer, cancellationToken));
}
// IObserver is a callback publisher
// Note: IObserver's basic scheme is "OnNext* (OnError | Oncompleted)?"
static IEnumerator GetWWWCore(string url, IObserver<string> observer, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var www = new UnityEngine.WWW(url);
while (!www.isDone && !cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
yield return null;
}
if (cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested) yield break;
if (www.error != null)
{
observer.OnError(new Exception(www.error));
}
else
{
observer.OnNext(www.text);
observer.OnCompleted(); // IObserver needs OnCompleted after OnNext!
}
}
这有一些例子。接下来是一个多OnNext模式。
public static IObservable<float> ToObservable(this UnityEngine.AsyncOperation asyncOperation)
{
if (asyncOperation == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("asyncOperation");
return Observable.FromCoroutine<float>((observer, cancellationToken) => RunAsyncOperation(asyncOperation, observer, cancellationToken));
}
static IEnumerator RunAsyncOperation(UnityEngine.AsyncOperation asyncOperation, IObserver<float> observer, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
while (!asyncOperation.isDone && !cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
observer.OnNext(asyncOperation.progress);
yield return null;
}
if (!cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
observer.OnNext(asyncOperation.progress); // push 100%
observer.OnCompleted();
}
}
// usecase
Application.LoadLevelAsync("testscene")
.ToObservable()
.Do(x => Debug.Log(x)) // output progress
.Last() // last sequence is load completed
.Subscribe();
用于多线程
// Observable.Start is start factory methods on specified scheduler
// default is on ThreadPool
var heavyMethod = Observable.Start(() =>
{
// heavy method...
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1));
return 10;
});
var heavyMethod2 = Observable.Start(() =>
{
// heavy method...
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3));
return 10;
});
// Join and await two other thread values
Observable.WhenAll(heavyMethod, heavyMethod2)
.ObserveOnMainThread() // return to main thread
.Subscribe(xs =>
{
// Unity can't touch GameObject from other thread
// but use ObserveOnMainThread, you can touch GameObject naturally.
(GameObject.Find("myGuiText")).guiText.text = xs[0] + ":" + xs[1];
});
默认调度器
UniRx 中基于时间的操作(Interval, Timer, Buffer(timeSpan), etc) 使用 Scheduler.MainThread 作为他们的默认调度器。这意味大多数操作符(除了Observable.Start)在单线程上工作,所以 ObserverOn 不是必须的而且不需要处理线程安全。这和标准的 RxNet 不太一样,但是更符合Unity环境。
Scheduler.MainThread 会受 Time.timeScale 的影响。如果你想要忽略time scale,使用 Scheduler.MainThreadIgnoreTimeScale 。
MonoBehaviour的触发器
使用 UniRx.Triggers 可以处理Monobehaviour的事件:
using UniRx;
using UniRx.Triggers; // need UniRx.Triggers namespace
public class MyComponent : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
// Get the plain object
var cube = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Cube);
// Add ObservableXxxTrigger for handle MonoBehaviour's event as Observable
cube.AddComponent<ObservableUpdateTrigger>()
.UpdateAsObservable()
.SampleFrame(30)
.Subscribe(x => Debug.Log("cube"), () => Debug.Log("destroy"));
// destroy after 3 second:)
GameObject.Destroy(cube, 3f);
}
}
支持的触发器列表 UniRx.wiki#UniRx.Triggers.
通过订阅Component/GameObject的扩展方法,控制这些触发器可以更简单。这些方法会自动添加ObservableTrigger到物体上(除了 ObservableEventTrigger and ObservableStateMachineTrigger):
using UniRx;
using UniRx.Triggers; // need UniRx.Triggers namespace for extend gameObejct
public class DragAndDropOnce : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
// All events can subscribe by ***AsObservable
this.OnMouseDownAsObservable()
.SelectMany(_ => this.UpdateAsObservable())
.TakeUntil(this.OnMouseUpAsObservable())
.Select(_ => Input.mousePosition)
.Subscribe(x => Debug.Log(x));
}
}
之前的UniRx提供了 ObservableMonoBehaviour。这是一个不再支持的过时的接口。请使用 UniRx.Triggers 代替。
创建自定义的触发器
处理Unity的事件的最好办法是转成Observable。如果UniRx自带的触发器还不够的话,你也可以自己创建触发器。下面是一个UGUI的长按触发器:
public class ObservableLongPointerDownTrigger : ObservableTriggerBase, IPointerDownHandler, IPointerUpHandler
{
public float IntervalSecond = 1f;
Subject<Unit> onLongPointerDown;
float? raiseTime;
void Update()
{
if (raiseTime != null && raiseTime <= Time.realtimeSinceStartup)
{
if (onLongPointerDown != null) onLongPointerDown.OnNext(Unit.Default);
raiseTime = null;
}
}
void IPointerDownHandler.OnPointerDown(PointerEventData eventData)
{
raiseTime = Time.realtimeSinceStartup + IntervalSecond;
}
void IPointerUpHandler.OnPointerUp(PointerEventData eventData)
{
raiseTime = null;
}
public IObservable<Unit> OnLongPointerDownAsObservable()
{
return onLongPointerDown ?? (onLongPointerDown = new Subject<Unit>());
}
protected override void RaiseOnCompletedOnDestroy()
{
if (onLongPointerDown != null)
{
onLongPointerDown.OnCompleted();
}
}
}
使用起来和自带触发器一样简单:
var trigger = button.AddComponent<ObservableLongPointerDownTrigger>();
trigger.OnLongPointerDownAsObservable().Subscribe();
Observable 生命周期管理
OnCompleted 什么时候会被调用?使用UniRx的时候Subscription的生命周期管理非常重要。ObservableTriggers 在attached的物体被销毁的时候调用。其他静态的方法 (Observable.Timer, Observable.EveryUpdate, etc…) 不会自动停止,需要手动去管理。
Rx 提供了一些方法, 例如 IDisposable.AddTo 可以让你一次性释放多个subscriptions:
// CompositeDisposable is similar with List<IDisposable>, manage multiple IDisposable
CompositeDisposable disposables = new CompositeDisposable(); // field
void Start()
{
Observable.EveryUpdate().Subscribe(x => Debug.Log(x)).AddTo(disposables);
}
void OnTriggerEnter(Collider other)
{
// .Clear() => Dispose is called for all inner disposables, and the list is cleared.
// .Dispose() => Dispose is called for all inner disposables, and Dispose is called immediately after additional Adds.
disposables.Clear();
}
如果你想在物体销毁时自动释放,可以用AddTo(GameObject/Component):
void Start()
{
Observable.IntervalFrame(30).Subscribe(x => Debug.Log(x)).AddTo(this);
}
AddTo 方法可以带来自动释放。如果你需要一些特殊的 OnCompleted 处理,使用 TakeWhile, TakeUntil, TakeUntilDestroy 或 TakeUntilDisable :
Observable.IntervalFrame(30).TakeUntilDisable(this)
.Subscribe(x => Debug.Log(x), () => Debug.Log("completed!"));
处理事件时,Repeat 时一个重要但是很危险的方法。可能会造成死循环,一定要小心处理:
using UniRx;
using UniRx.Triggers;
public class DangerousDragAndDrop : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
this.gameObject.OnMouseDownAsObservable()
.SelectMany(_ => this.gameObject.UpdateAsObservable())
.TakeUntil(this.gameObject.OnMouseUpAsObservable())
.Select(_ => Input.mousePosition)
.Repeat() // dangerous!!! Repeat cause infinite repeat subscribe at GameObject was destroyed.(If in UnityEditor, Editor is freezed)
.Subscribe(x => Debug.Log(x));
}
}
UniRx额外提供了一个安全的Repeat方法。RepeatSafe: 如果”OnComplete”连续调用,Repeat会自动停止。 RepeatUntilDestroy(gameObject/component), RepeatUntilDisable(gameObject/component) 可以在gameobject被销毁时停止Repeat:
this.gameObject.OnMouseDownAsObservable()
.SelectMany(_ => this.gameObject.UpdateAsObservable())
.TakeUntil(this.gameObject.OnMouseUpAsObservable())
.Select(_ => Input.mousePosition)
.RepeatUntilDestroy(this) // safety way
.Subscribe(x => Debug.Log(x));
UniRx保证动态observable(FromEvent/Subject/ReactiveProperty/UnityUI.AsObservable…, there are like event) 内有未处理的异常时也能持续工作。什么意思呢?如果在Subscribe内subscribe,里面subscribe的异样不会造成外部的subscribe失效。
button.OnClickAsObservable().Subscribe(_ =>
{
// If throws error in inner subscribe, but doesn't detached OnClick event.
ObservableWWW.Get("htttp://error/").Subscribe(x =>
{
Debug.Log(x);
});
});
这样在处理用户事件时很有用。
所有类的实例提供了一个 ObserveEveryValueChanged 方法,可以在每帧监听值的变化:
// watch position change
this.transform.ObserveEveryValueChanged(x => x.position).Subscribe(x => Debug.Log(x));
这很有用。如果监听的目标是一个GameObject, 会在目标被销毁时停止并调用OnCompleted。如果监听目标是C#的对象,OnCompleted会在GC时调用。
将Unity回调转为IObservable
使用Subject (或AsyncSubject用于异步操作):
public class LogCallback
{
public string Condition;
public string StackTrace;
public UnityEngine.LogType LogType;
}
public static class LogHelper
{
static Subject<LogCallback> subject;
public static IObservable<LogCallback> LogCallbackAsObservable()
{
if (subject == null)
{
subject = new Subject<LogCallback>();
// Publish to Subject in callback
UnityEngine.Application.RegisterLogCallback((condition, stackTrace, type) =>
{
subject.OnNext(new LogCallback { Condition = condition, StackTrace = stackTrace, LogType = type });
});
}
return subject.AsObservable();
}
}
// method is separatable and composable
LogHelper.LogCallbackAsObservable()
.Where(x => x.LogType == LogType.Warning)
.Subscribe();
LogHelper.LogCallbackAsObservable()
.Where(x => x.LogType == LogType.Error)
.Subscribe();
Unity5中移除了 Application.RegisterLogCallback,并用 Application.logMessageReceived替代。所以可以更简单地用 Observable.FromEvent。
public static IObservable<LogCallback> LogCallbackAsObservable()
{
return Observable.FromEvent<Application.LogCallback, LogCallback>(
h => (condition, stackTrace, type) => h(new LogCallback { Condition = condition, StackTrace = stackTrace, LogType = type }),
h => Application.logMessageReceived += h, h => Application.logMessageReceived -= h);
}
流式日志记录器Stream Logger
// using UniRx.Diagnostics;
// logger is threadsafe, define per class with name.
static readonly Logger logger = new Logger("Sample11");
// call once at applicationinit
public static void ApplicationInitialize()
{
// Log as Stream, UniRx.Diagnostics.ObservableLogger.Listener is IObservable<LogEntry>
// You can subscribe and output to any place.
ObservableLogger.Listener.LogToUnityDebug();
// for example, filter only Exception and upload to web.
// (make custom sink(IObserver<EventEntry>) is better to use)
ObservableLogger.Listener
.Where(x => x.LogType == LogType.Exception)
.Subscribe(x =>
{
// ObservableWWW.Post("", null).Subscribe();
});
}
// Debug is write only DebugBuild.
logger.Debug("Debug Message");
// or other logging methods
logger.Log("Message");
logger.Exception(new Exception("test exception"));
调试Debugging
UniRx.Diagnostics 中的 Debug 操作符可以帮助调试。
// needs Diagnostics using
using UniRx.Diagnostics;
---
// [DebugDump, Normal]OnSubscribe
// [DebugDump, Normal]OnNext(1)
// [DebugDump, Normal]OnNext(10)
// [DebugDump, Normal]OnCompleted()
{
var subject = new Subject<int>();
subject.Debug("DebugDump, Normal").Subscribe();
subject.OnNext(1);
subject.OnNext(10);
subject.OnCompleted();
}
// [DebugDump, Cancel]OnSubscribe
// [DebugDump, Cancel]OnNext(1)
// [DebugDump, Cancel]OnCancel
{
var subject = new Subject<int>();
var d = subject.Debug("DebugDump, Cancel").Subscribe();
subject.OnNext(1);
d.Dispose();
}
// [DebugDump, Error]OnSubscribe
// [DebugDump, Error]OnNext(1)
// [DebugDump, Error]OnError(System.Exception)
{
var subject = new Subject<int>();
subject.Debug("DebugDump, Error").Subscribe();
subject.OnNext(1);
subject.OnError(new Exception());
}
将按事件顺序显示 OnNext, OnError, OnCompleted, OnCancel, OnSubscribe 的调用并通过Debug.Log打印出来。只在 #if DEBUG时生效。
译者注:SubscribeOnMainThread()经测试现在没有效果,有BUG(2018年1月30日,UniRx版本5.5)
// Unity's singleton UiThread Queue Scheduler
Scheduler.MainThreadScheduler
ObserveOnMainThread()/SubscribeOnMainThread()
// Global StartCoroutine runner
MainThreadDispatcher.StartCoroutine(enumerator)
// convert Coroutine to IObservable
Observable.FromCoroutine((observer, token) => enumerator(observer, token));
// convert IObservable to Coroutine
yield return Observable.Range(1, 10).ToYieldInstruction(); // after Unity 5.3, before can use StartAsCoroutine()
// Lifetime hooks
Observable.EveryApplicationPause();
Observable.EveryApplicationFocus();
Observable.OnceApplicationQuit();
Framecount-based time operators(基于帧数的时间操作)
UniRx 提供了一些基于帧数的时间操作:
| Method |
| EveryUpdate |
| EveryFixedUpdate |
| EveryEndOfFrame |
| EveryGameObjectUpdate |
| EveryLateUpdate |
| ObserveOnMainThread |
| NextFrame |
| IntervalFrame |
| TimerFrame |
| DelayFrame |
| SampleFrame |
| ThrottleFrame |
| ThrottleFirstFrame |
| TimeoutFrame |
| DelayFrameSubscription |
| FrameInterval |
| FrameTimeInterval |
| BatchFrame |
例如,一次延迟调用:
Observable.TimerFrame(100).Subscribe(_ => Debug.Log("after 100 frame"));
Every* 方法们的执行顺序是
EveryGameObjectUpdate(in MainThreadDispatcher's Execution Order) ->
EveryUpdate ->
EveryLateUpdate ->
EveryEndOfFrame
EveryGameObjectUpdate 在同一帧被调用,从 MainThreadDispatcher.Update 中调用(作者建议 MainThreadDispatcher 脚本比其他脚本先执行(ScriptExecutionOrder 设置为 -32000)
EveryLateUpdate, EveryEndOfFrame 在同一帧调用。
然后在下一帧调用EveryGameObjectUpdate,以此类推
MicroCoroutine(微协程)
MicroCoroutine 在内存上更有效率,而且更快。这是基于Unity的这篇博客《10000 UPDATE() CALLS》(http://blogs.unity3d.com/2015/12/23/1k-update-calls/)实现的,可以快上几十倍。MicroCoroutine会自动用于基于帧数的时间操作和ObserveEveryValueChanged。
如果你想要使用MicroCoroutine替代unity内置的协程,使用 MainThreadDispatcher.StartUpdateMicroCoroutine 或者 Observable.FromMicroCoroutine。
int counter;
IEnumerator Worker()
{
while(true)
{
counter++;
yield return null;
}
}
void Start()
{
for(var i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
// fast, memory efficient
MainThreadDispatcher.StartUpdateMicroCoroutine(Worker());
// slow...
// StartCoroutine(Worker());
}
}

MicroCoroutine的局限是:仅支持 yield return null 并且调用的时间是根据调用的方法来确定(StartUpdateMicroCoroutine, StartFixedUpdateMicroCoroutine, StartEndOfFrameMicroCoroutine).。
如果和其他IObservable一起用,你可以检查完成属性比如isDone。
IEnumerator MicroCoroutineWithToYieldInstruction()
{
var www = ObservableWWW.Get("http://aaa").ToYieldInstruction();
while (!www.IsDone)
{
yield return null;
}
if (www.HasResult)
{
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(www.Result);
}
}
uGUI集成
UniRx处理UnityEvent很简单。使用UnityEvent.AsObservable订阅事件。
public Button MyButton;
// ---
MyButton.onClick.AsObservable().Subscribe(_ => Debug.Log("clicked"));
将事件转为Observables,这样就可以用声名式UI编程。
public Toggle MyToggle;
public InputField MyInput;
public Text MyText;
public Slider MySlider;
// On Start, you can write reactive rules for declaretive/reactive ui programming
void Start()
{
// Toggle, Input etc as Observable (OnValueChangedAsObservable is a helper providing isOn value on subscribe)
// SubscribeToInteractable is an Extension Method, same as .interactable = x)
MyToggle.OnValueChangedAsObservable().SubscribeToInteractable(MyButton);
// Input is displayed after a 1 second delay
MyInput.OnValueChangedAsObservable()
.Where(x => x != null)
.Delay(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1))
.SubscribeToText(MyText); // SubscribeToText is helper for subscribe to text
// Converting for human readability
MySlider.OnValueChangedAsObservable()
.SubscribeToText(MyText, x => Math.Round(x, 2).ToString());
}
更多的响应式UI编程参见工程中例子Sample12, Sample13以及下面ReactiveProperty部分。
ReactiveProperty, ReactiveCollection
游戏数据变化时通常需要通知别的类。我们应该用属性和事件(回调)么?这通常太繁琐了。UniRx提供了ReactiveProperty类,一个轻量的属性代理。
// Reactive Notification Model
public class Enemy
{
public ReactiveProperty<long> CurrentHp { get; private set; }
public ReactiveProperty<bool> IsDead { get; private set; }
public Enemy(int initialHp)
{
// Declarative Property
CurrentHp = new ReactiveProperty<long>(initialHp);
IsDead = CurrentHp.Select(x => x <= 0).ToReactiveProperty();
}
}
// ---
// onclick, HP decrement
MyButton.OnClickAsObservable().Subscribe(_ => enemy.CurrentHp.Value -= 99);
// subscribe from notification model.
enemy.CurrentHp.SubscribeToText(MyText);
enemy.IsDead.Where(isDead => isDead == true)
.Subscribe(_ =>
{
MyButton.interactable = false;
});
你可以用UnityEvent.AsObservable将ReactiveProperties, ReactiveCollections 和 observables 组合起来。 所有UI组件都是observable的。
一般来说ReactiveProperties不是可序列化的或者说在Unity编辑器的Inspector面板中看不到,但是UniRx提供了特殊的子类来实现这个功能。包括Int/LongReactiveProperty, Float/DoubleReactiveProperty, StringReactiveProperty, BoolReactiveProperty,还有更多参见:InspectableReactiveProperty.cs(https://github.com/neuecc/UniRx/blob/master/Assets/Plugins/UniRx/Scripts/UnityEngineBridge/InspectableReactiveProperty.cs))。都可以在Inspector中编辑。对于自定义的枚举ReactiveProperty,写一个可检视的ReactiveProperty[T]也很容易。
如果你需要[Multiline] 或者 [Range] 添加到ReactiveProperty上,你可以使用 MultilineReactivePropertyAttribute和 RangeReactivePropertyAttribute 替换 Multiline 和 Range。
这些InpsectableReactiveProperties可以在inspector面板显示,并且当他们的值发生变化时发出通知,甚至在编辑器里变化时也可以。

这个功能是实现在 InspectorDisplayDrawer (https://github.com/neuecc/UniRx/blob/master/Assets/Plugins/UniRx/Scripts/UnityEngineBridge/InspectorDisplayDrawer.cs)。你可以通过继承这个类实现你自定义的ReactiveProperties在inspector面板的绘制:
public enum Fruit
{
Apple, Grape
}
[Serializable]
public class FruitReactiveProperty : ReactiveProperty<Fruit>
{
public FruitReactiveProperty()
{
}
public FruitReactiveProperty(Fruit initialValue)
:base(initialValue)
{
}
}
[UnityEditor.CustomPropertyDrawer(typeof(FruitReactiveProperty))]
[UnityEditor.CustomPropertyDrawer(typeof(YourSpecializedReactiveProperty2))] // and others...
public class ExtendInspectorDisplayDrawer : InspectorDisplayDrawer
{
}
如果ReactiveProperty的值只在stream中更新,你可以用 ReadOnlyReactiveProperty 让这个属性只读。
public class Person
{
public ReactiveProperty<string> GivenName { get; private set; }
public ReactiveProperty<string> FamilyName { get; private set; }
public ReadOnlyReactiveProperty<string> FullName { get; private set; }
public Person(string givenName, string familyName)
{
GivenName = new ReactiveProperty<string>(givenName);
FamilyName = new ReactiveProperty<string>(familyName);
// If change the givenName or familyName, notify with fullName!
FullName = GivenName.CombineLatest(FamilyName, (x, y) => x + " " + y).ToReadOnlyReactiveProperty();
}
}
MVP设计模式 Model-View-(Reactive)Presenter Pattern
用UniRx可以实现MVP(MVRP)设计模式。

为什么应该用MVP模式而不是MVVM模式?Unity没有提供UI绑定机制,创建一个绑定层过于复杂并且会对性能造成影响。 尽管如此,视图还是需要更新。Presenters层知道view的组件并且能更新它们。虽然没有真的绑定,但Observables可以通知订阅者,功能上也差不多。这种模式叫做Reactive Presenter:
// Presenter for scene(canvas) root.
public class ReactivePresenter : MonoBehaviour
{
// Presenter is aware of its View (binded in the inspector)
public Button MyButton;
public Toggle MyToggle;
// State-Change-Events from Model by ReactiveProperty
Enemy enemy = new Enemy(1000);
void Start()
{
// Rx supplies user events from Views and Models in a reactive manner
MyButton.OnClickAsObservable().Subscribe(_ => enemy.CurrentHp.Value -= 99);
MyToggle.OnValueChangedAsObservable().SubscribeToInteractable(MyButton);
// Models notify Presenters via Rx, and Presenters update their views
enemy.CurrentHp.SubscribeToText(MyText);
enemy.IsDead.Where(isDead => isDead == true)
.Subscribe(_ =>
{
MyToggle.interactable = MyButton.interactable = false;
});
}
}
// The Model. All property notify when their values change
public class Enemy
{
public ReactiveProperty<long> CurrentHp { get; private set; }
public ReactiveProperty<bool> IsDead { get; private set; }
public Enemy(int initialHp)
{
// Declarative Property
CurrentHp = new ReactiveProperty<long>(initialHp);
IsDead = CurrentHp.Select(x => x <= 0).ToReactiveProperty();
}
}
视图层是一个场景scene,是Unity的hierachy定义的。展示层在Unity初始化时将视图层绑定。XxxAsObservable方法可以很容易的创建事件信号signals,没有任何开销。SubscribeToText and SubscribeToInteractable 都是简洁的类似绑定的辅助函数。虽然这些工具很简单,但是非常有用。在Unity中使用很平滑,性能很好,而且让你的代码更简洁。

V -> RP -> M -> RP -> V 完全用响应式的方式连接。UniRx提供了所有的适配方法和类,不过其他的MVVM(or MV*)框架也可以使用。UniRx/ReactiveProperty只是一个简单的工具包。
GUI编程也可以从ObservableTriggers获益良多。ObservableTriggers将Unity事件转为Observables,所以MV(R)P模式可以用它们来组成。例如 ObservableEventTrigger 将 uGUI 事件转为 Observable:
var eventTrigger = this.gameObject.AddComponent<ObservableEventTrigger>();
eventTrigger.OnBeginDragAsObservable()
.SelectMany(_ => eventTrigger.OnDragAsObservable(), (start, current) => UniRx.Tuple.Create(start, current))
.TakeUntil(eventTrigger.OnEndDragAsObservable())
.RepeatUntilDestroy(this)
.Subscribe(x => Debug.Log(x));
(已过时)PresenterBase
备注:
PresenterBase有用,不过太复杂了
你可以仅用 Initialize 方法,在子类中调用父类就足够应付大多数情况了。
所以不再建议使用 PresenterBase。
ReactiveCommand, AsyncReactiveCommand
ReactiveCommand 抽象了按钮的interactable属性。
public class Player
{
public ReactiveProperty<int> Hp;
public ReactiveCommand Resurrect;
public Player()
{
Hp = new ReactiveProperty<int>(1000);
// If dead, can not execute.
Resurrect = Hp.Select(x => x <= 0).ToReactiveCommand();
// Execute when clicked
Resurrect.Subscribe(_ =>
{
Hp.Value = 1000;
});
}
}
public class Presenter : MonoBehaviour
{
public Button resurrectButton;
Player player;
void Start()
{
player = new Player();
// If Hp <= 0, can't press button.
player.Resurrect.BindTo(resurrectButton);
}
}
AsyncReactiveCommand是ReactiveCommand的变种,它的 CanExecute (通常绑定到button的interactable) 在异步操作完成后变为false。
public class Presenter : MonoBehaviour
{
public UnityEngine.UI.Button button;
void Start()
{
var command = new AsyncReactiveCommand();
command.Subscribe(_ =>
{
// heavy, heavy, heavy method....
return Observable.Timer(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3)).AsUnitObservable();
});
// after clicked, button shows disable for 3 seconds
command.BindTo(button);
// Note:shortcut extension, bind aync onclick directly
button.BindToOnClick(_ =>
{
return Observable.Timer(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3)).AsUnitObservable();
});
}
}
AsyncReactiveCommand 有三个构造方法。
() – CanExecute is changed to false until async execution finished(IObservable<bool> canExecuteSource) – 当 canExecuteSource 变为 true 并且没有在执行的时候 CanExecute 变为true 。(IReactiveProperty<bool> sharedCanExecute) – 在多个AsyncReactiveCommands之间共享运行状态,如果一个 AsyncReactiveCommand 在执行,那么其他的 AsyncReactiveCommands(拥有相同 sharedCanExecute 属性) 的 CanExecute 变为 false 直到异步操作完成。
public class Presenter : MonoBehaviour
{
public UnityEngine.UI.Button button1;
public UnityEngine.UI.Button button2;
void Start()
{
// share canExecute status.
// when clicked button1, button1 and button2 was disabled for 3 seconds.
var sharedCanExecute = new ReactiveProperty<bool>();
button1.BindToOnClick(sharedCanExecute, _ =>
{
return Observable.Timer(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3)).AsUnitObservable();
});
button2.BindToOnClick(sharedCanExecute, _ =>
{
return Observable.Timer(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3)).AsUnitObservable();
});
}
}
MessageBroker, AsyncMessageBroker(消息代理,异步消息代理)
MessageBroker 是基于 Rx 的内存发布订阅(pubsub)系统,基于类型筛选。
public class TestArgs
{
public int Value { get; set; }
}
---
// Subscribe message on global-scope.
MessageBroker.Default.Receive<TestArgs>().Subscribe(x => UnityEngine.Debug.Log(x));
// Publish message
MessageBroker.Default.Publish(new TestArgs { Value = 1000 });
AsyncMessageBroker 是 MessageBroker 的一个变种, 可以处理异步的 Publish 调用。
AsyncMessageBroker.Default.Subscribe<TestArgs>(x =>
{
// show after 3 seconds.
return Observable.Timer(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3))
.ForEachAsync(_ =>
{
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(x);
});
});
AsyncMessageBroker.Default.PublishAsync(new TestArgs { Value = 3000 })
.Subscribe(_ =>
{
UnityEngine.Debug.Log("called all subscriber completed");
});
UniRx.Toolkit 包含了一些Rx风格的工具。目前报错 ObjectPool 和 AsyncObjectPool。可以 Rent, Return and PreloadAsync (在rent操作之前预加载对象池)。
// sample class
public class Foobar : MonoBehaviour
{
public IObservable<Unit> ActionAsync()
{
// heavy, heavy, action...
return Observable.Timer(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3)).AsUnitObservable();
}
}
public class FoobarPool : ObjectPool<Foobar>
{
readonly Foobar prefab;
readonly Transform hierarchyParent;
public FoobarPool(Foobar prefab, Transform hierarchyParent)
{
this.prefab = prefab;
this.hierarchyParent = hierarchyParent;
}
protected override Foobar CreateInstance()
{
var foobar = GameObject.Instantiate<Foobar>(prefab);
foobar.transform.SetParent(hierarchyParent);
return foobar;
}
// You can overload OnBeforeRent, OnBeforeReturn, OnClear for customize action.
// In default, OnBeforeRent = SetActive(true), OnBeforeReturn = SetActive(false)
// protected override void OnBeforeRent(Foobar instance)
// protected override void OnBeforeReturn(Foobar instance)
// protected override void OnClear(Foobar instance)
}
public class Presenter : MonoBehaviour
{
FoobarPool pool = null;
public Foobar prefab;
public Button rentButton;
void Start()
{
pool = new FoobarPool(prefab, this.transform);
rentButton.OnClickAsObservable().Subscribe(_ =>
{
var foobar = pool.Rent();
foobar.ActionAsync().Subscribe(__ =>
{
// if action completed, return to pool
pool.Return(foobar);
});
});
}
}
Visual Studio 分析器
Visual Studio 2015的用户可以使用一个分析器UniRxAnalyzer。它可以检测没有被subscribed的streams。


ObservableWWW 直到subscribed才会执行,所以分析器会发出警告。分析器可以从NuGet下载。
请在GitHub Issues上提交对分析器的新想法!
例子
参见 UniRx/Examples(https://github.com/neuecc/UniRx/tree/master/Assets/Plugins/UniRx/Examples)
Sample09_EventHandling 展示了如何进行资源管理,包括MainThreadDispatcher和其他一些东西。
Windows Store/Phone App (NETFX_CORE)
一些接口,如 UniRx.IObservable<T> and System.IObservable<T> 在Windows Store App中使用时会造成冲突。
因此,如果使用 NETFX_CORE,避免使用类似 UniRx.IObservable<T> 的构造器,避免不加命名空间使用UniRx组件。这样可以解决冲突问题。
async/await Support
基于 《Upgraded Mono/.Net in Editor on 5.5.0b4》(https://forum.unity3d.com/threads/upgraded-mono-net-in-editor-on-5-5-0b4.433541/),Unity支持了 .NET 4.6 和 C# 6。UniRx 提供了 UniRxSynchronizationContext 来将多线程的任务返回到主线程。
async Task UniRxSynchronizationContextSolves()
{
Debug.Log("start delay");
// UniRxSynchronizationContext is automatically used.
await Task.Delay(TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(300));
Debug.Log("from another thread, but you can touch transform position.");
Debug.Log(this.transform.position);
}
UniRx 也直接支持 await Coroutine。
async Task CoroutineBridge()
{
Debug.Log("start www await");
var www = await new WWW("https://unity3d.com");
Debug.Log(www.text);
}
当然了,IObservable可是可以await的。
async Task AwaitObservable()
{
Debug.Log("start await observable");
await Observable.NextFrame(); // like yield return null
await Observable.TimerFrame(5); // await 5 frame
Debug.Log("end await observable");
}
DLL分割
如果你想预编译UniRx,你可以自行编译dll。clone这个project,打开 UniRx.sln, 你可以看到 UniRx, 是一个完全独立的工程。你应该定义一些宏如 UNITY;UNITY_5_4_OR_NEWER;UNITY_5_4_0;UNITY_5_4;UNITY_5; + UNITY_EDITOR, UNITY_IPHONE或这其他平台宏。我们没法提供预编译的dll,因为不同版本Unity的宏是不一样的。
如果你想将UniRx用于.NET 3.5 CLR应用,你可以使用UniRx.Library。 UniRx.Library 不依赖UnityEngine,编译 UniRx.Library 需要定义 UniRxLibrary 宏。另外预编译的 UniRx.Library 库可以在NuGet获取到。
Install-Package UniRx(https://www.nuget.org/packages/UniRx)
其他参考
UniRx API文档。
The home of ReactiveX. Introduction, All operators are illustrated with graphical marble diagrams, there makes easy to understand. And UniRx is official ReactiveX Languages.
A great online tutorial and eBook.
Many videos, slides and documents for Rx.NET.
Intro slide by @torisoup
Intro slide and sample game by @Xerios
How to integrate with PlayFab API
What game or library is using UniRx?
Games
– [Farm Away!][(http://www.farmawaygame.com/)
– Build Away!
– AdVenture Capitalist
– AdVenture Communist
Libraries
- PhotonWire – Typed Asynchronous RPC Layer for Photon Server + Unity.
- uFrame Game Framework – MVVM/MV* framework designed for the Unity Engine.
- EcsRx – A simple framework for unity using the ECS paradigm but with unirx for fully reactive systems.
- ActionStreetMap Demo – ASM is an engine for building real city environment dynamically using OSM data.
- utymap – UtyMap is library for building real city environment dynamically using various data sources (mostly, OpenStreetMap and Natural Earth).
- Submarine – A mobile game that is made with Unity3D and RoR, WebSocket server written in Go.
If you use UniRx, please comment to UniRx/issues/152.
Help & Contribute
Support thread on the Unity forum. Ask me any question – http://forum.unity3d.com/threads/248535-UniRx-Reactive-Extensions-for-Unity
We welcome any contributions, be they bug reports, requests or pull request.
Please consult and submit your reports or requests on GitHub issues.
Source code is available in Assets/Plugins/UniRx/Scripts.
This project is using Visual Studio with UnityVS.
Author’s other Unity + LINQ Assets
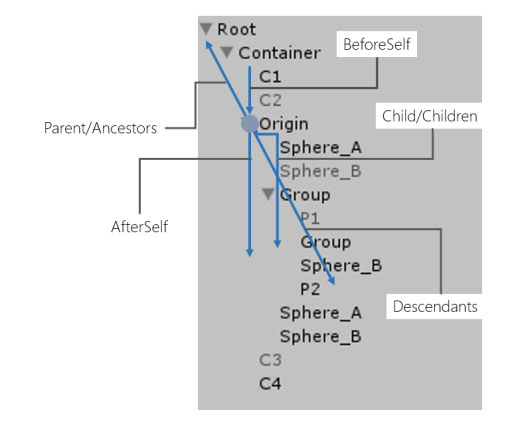
LINQ to GameObject is a group of GameObject extensions for Unity that allows traversing the hierarchy and appending GameObject to it like LINQ to XML. It’s free and opensource on GitHub.
Author Info
Yoshifumi Kawai(a.k.a. neuecc) is a software developer in Japan.
He is the Director/CTO at Grani, Inc.
Grani is a top social game developer in Japan.
He is awarding Microsoft MVP for Visual C# since 2011.
He is known as the creator of linq.js(LINQ to Objects for JavaScript)
Blog: https://medium.com/@neuecc (English)
Blog: http://neue.cc/ (Japanese)
Twitter: https://twitter.com/neuecc (Japanese)
License
This library is under the MIT License.
Some code is borrowed from Rx.NET and mono/mcs.














